Overtraining refers to a training cycle of approximately, leading to a state of excessive fatigue and reduced performance. Understanding the causes, consequences, and recovery methods of overtraining is crucial for athletes and fitness enthusiasts alike.
Overtraining: Definition and Causes: Overtraining Refers To A Training Cycle Of Approximately
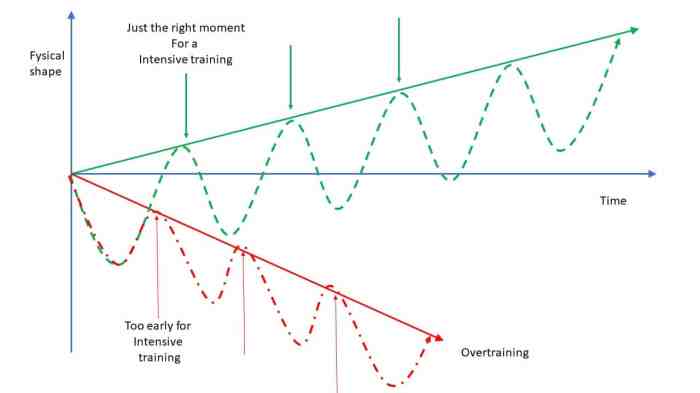
Overtraining refers to a training cycle of approximately 6 weeks or more, characterized by excessive training volume, intensity, and duration, leading to a state of chronic fatigue and impaired performance. Symptoms include persistent muscle soreness, decreased motivation, disrupted sleep patterns, and increased susceptibility to injuries.
The physiological causes of overtraining include muscle damage, hormonal imbalances, and immune suppression. The psychological causes include burnout, depression, and anxiety.
Consequences of Overtraining
Overtraining can have severe negative impacts on physical performance, including decreased strength, endurance, and power. It can also lead to hormonal imbalances, such as decreased testosterone and increased cortisol levels, which further impair performance and recovery. Overtraining suppresses the immune system, increasing the risk of infections and illnesses.
Additionally, overtraining can have significant mental and emotional consequences, including burnout, depression, and anxiety.
Diagnosis and Prevention of Overtraining, Overtraining refers to a training cycle of approximately
Diagnosing overtraining can be challenging, as it requires a comprehensive evaluation of physical, physiological, and psychological factors. Physical exams, blood tests, and questionnaires can help identify signs of overtraining. Prevention strategies include gradual training progression, adequate rest and recovery, and monitoring training load.
Individualized training plans tailored to each athlete’s needs and goals are crucial. Coaches and healthcare professionals play a vital role in monitoring athletes and providing support to prevent overtraining.
Recovery from Overtraining
Recovery from overtraining requires a multifaceted approach. Rest is essential, with a gradual reduction in training intensity and volume. Proper nutrition is vital to support recovery and repair. Physical therapy, massage, and other recovery modalities can aid in reducing muscle soreness and promoting relaxation.
Gradual return to training is crucial, with close monitoring to prevent relapse. The recovery process can take several weeks or months, depending on the severity of overtraining.
FAQ Overview
What are the key symptoms of overtraining?
Persistent fatigue, decreased performance, muscle soreness, sleep disturbances, and mood changes.
How can overtraining be prevented?
Gradual training progression, adequate rest and recovery, monitoring training load, and individualized training plans.
What is the recommended recovery process for overtraining?
Rest, reduced training intensity, proper nutrition, physical therapy, massage, and gradual return to training.

